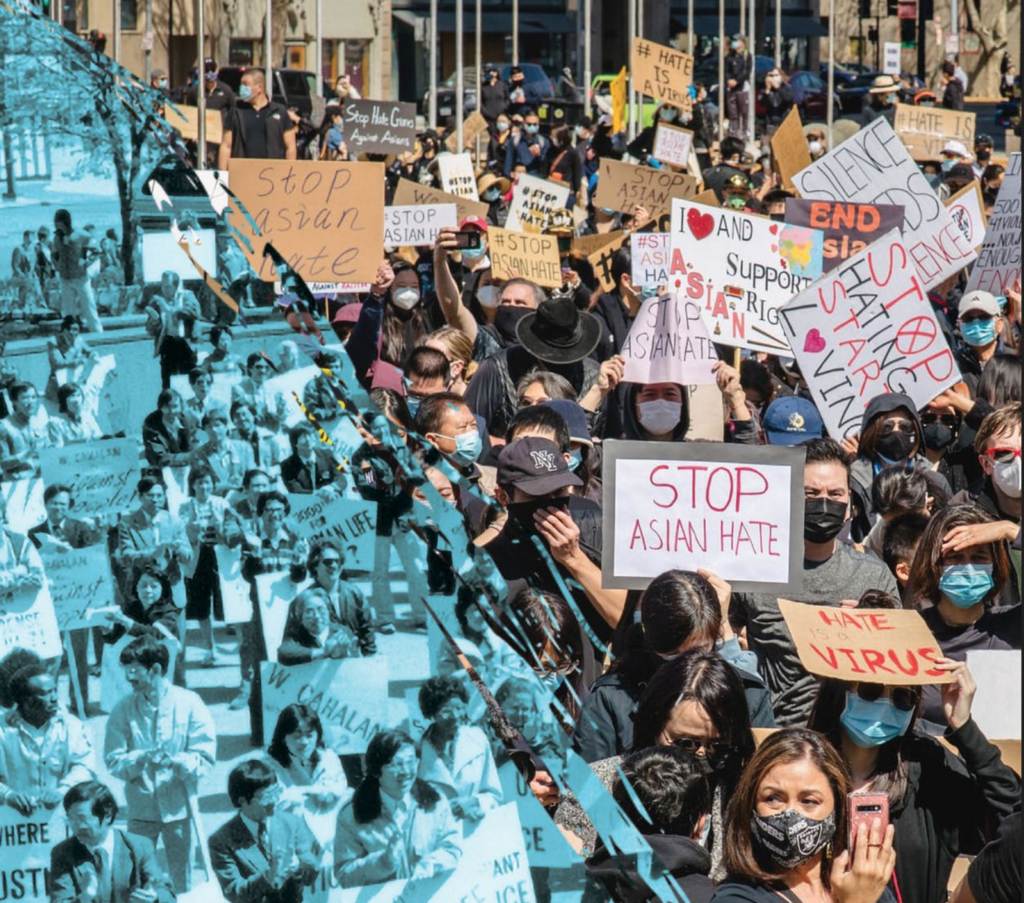
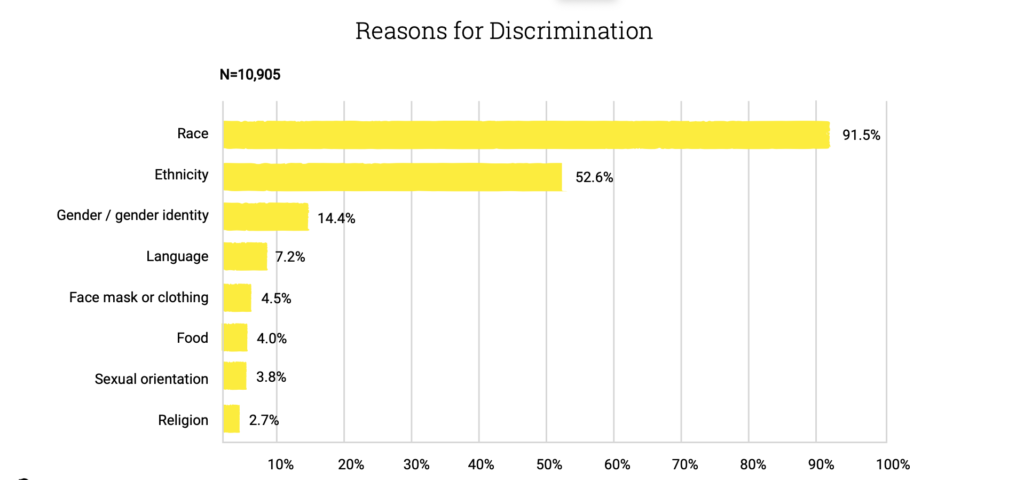
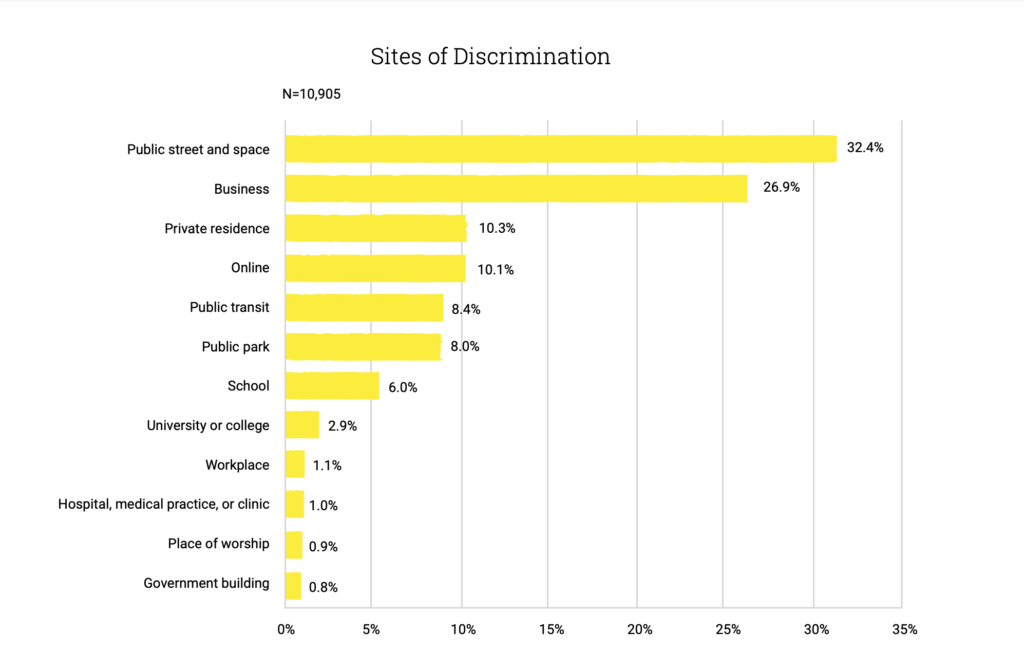
As stated by Vadala, “shamanism is a “universal singularity” or a religious form that can emerge and successfully gain a foothold in a given society when the religious system and social order are compatible with individual small-scale religious leadership. Such systems must require highly flexible social actors, like shamans, who can aid individuals (patients) and lead groups (apprentices and members of a community) in spiritual matters.”
(Vadala, 2019).
What is Shamanism?
Shamanism is a form of holistic healing that can be highly diverse; also, it is a spiritual practice found in cultures across the world from ancient times up to the present day. Shamanism is known for its holistic forms of religion, healing, and medicine. It combines the use of supernatural spiritual involvement and the usage of natural remedies. The Hmong community is one of the better-known groups that practice Shamanism. There are many responsibilities for the Shamans as chosen healers; also, they understand and know natural remedies. Sometimes, a shaman must negotiate with the spirit for a patient’s soul or well-being. Most traditional Hmong families or individuals might use shamans in combination with American or modern medicine. Additionally, shamans’ practices are adaptable and practical. These practices coexisted over millennia with government systems, organized religious traditions, and distinct cultures (Lawson,2016).

“Because it is not an organized religion as such, but rather a spiritual practice, Shamanism cuts across all faiths and creeds, reaching deep levels of ancestral memory. As a primal belief system, which precedes established religion, it has its own symbolism and cosmology, inhabited by beings, gods, and totems, who display similar characteristics. However, they appear in various forms, depending upon their places of origin.” ~John Matthews, The Celtic Shaman.
(Lawson,2016)
What is a shaman?
The definition of a shaman according to famed American psychologist and consciousness pioneer Stanley Krippner, shamans are “community-assigned magico-religious professionals who deliberately alter their consciousness in order to obtain information from the ‘spirit world.’ They use this knowledge and power to help and to heal members of their community, as well as the community as a whole” (Lawson,2016). Moreover, Krippner describes shamans as the first physicians, diagnosticians, psychotherapists, religious functionaries, magicians, performing artists, and storytellers (Lawson,2016). Based on the study in shamanistic cultures, all adults are responsible for their relationships with spiritual energies, including those of their ancestors, own personal helping spirits, the creator force, and their home environments, such as animals, plant life, and geography. Nevertheless, the shamans have increased the facility for traveling in non-ordinary realms and using their spirit relationships to create changes. These changes will manifest in the physical world to heal individuals and the community (Lawson,2016). Therefore, the cultural healers’ Hmong shamans can help the community recover from the pandemic through their knowledge and spiritual power.
Hmong Shaman and Herb Center (HSHC) has provided accessible shaman and herbal healing to Hmong families in the Twin Cities area since 2019. HSHC provides a unique healing space and direct services to clients. Also, they work to support Hmong families and try to make changes in the broader systems. Moreover, HSHC has the mission to increase access to mental health support for Hmong families so that they may recover their lives from mental illnesses. To achieve HSHC goals, they do the following activities: outreach, education, training, deep practitioner development, and community partnerships at the intersection of healing and racial justice. HSHC offers substance use disorder services, coordinates with physical health care and social services, and provides integrated mental health.
Furthermore, HSHC is a designated organization to serve individuals of all ages regardless of their ability to pay and where they live. HSHC has the vision of empowering the Hmong community with holistic practices through Herbal medicine and Shamanism. Also, they help people to take charge of their wellness and health.
References
Vadala, J. (2019). Cross-culturally exploring the concept of shamanism. Human relations area files. https://hraf.yale.edu/cross-culturally-exploring-the-concept-of-shamanism/
Lawson, K. (2016).Shamanism. Taking charge of your health & wellbeing.